A shipment of frozen fish arrives at your food establishment – now what? This comprehensive guide navigates the entire process, from receiving the delicate cargo to ensuring optimal storage, quality control, and food safety. Get ready to learn the ins and outs of handling a frozen fish delivery like a pro! From unpacking to inventory, we’ll cover every step to make sure your fish is fresh and your business is running smoothly.
This detailed guide covers everything from the initial receiving process, including paperwork and temperature checks, to the critical steps of storage, handling, and quality control. It also addresses crucial aspects like food safety regulations, inventory management, and even the environmental impact of handling frozen fish. Let’s dive in!
Receiving the Shipment: A Shipment Of Frozen Fish Arrives At Your Food Establishment
Receiving a shipment of frozen fish is a critical process in a food establishment, impacting the quality and safety of the final product. Proper handling ensures that the fish remains at the required temperature, minimizing the risk of bacterial growth and maintaining its freshness. Adherence to established procedures is paramount for maintaining halal standards.
Ideal Receiving Process, A shipment of frozen fish arrives at your food establishment
The ideal process for receiving a shipment of frozen fish involves several key steps to ensure quality and safety. These steps are designed to maintain the integrity of the product, preserving its quality and ensuring that the product meets the necessary standards for halal consumption.
- Verification of Documentation: This is the first crucial step, requiring a thorough examination of the accompanying documents. These documents include the delivery note, invoice, and the cold chain certificate, which is crucial for verifying the adherence to the required temperature during transit. The cold chain certificate serves as a vital record of the temperature monitoring throughout the entire transportation process, ensuring the fish has been maintained at the correct temperature.
This process ensures that the shipment complies with all necessary regulations and requirements for halal food handling.
- Visual Inspection: A meticulous visual inspection of the fish is imperative. This step involves checking for any signs of damage, such as breakage, discoloration, or unusual odors. Damaged fish must be rejected immediately to avoid any potential health hazards or quality concerns. The fish should also be inspected for compliance with the establishment’s quality standards and specifications. The inspection ensures that the fish meets the expected quality parameters, maintaining its freshness and suitability for consumption.
- Temperature Check: The temperature of the fish must be recorded upon arrival to ensure that the fish has been stored and transported at the appropriate temperature throughout the journey. A thermometer should be used to measure the temperature of the fish’s packaging. This is crucial for maintaining the safety and quality of the product, preventing bacterial growth and upholding halal standards.
A shipment of frozen fish has arrived at the establishment. To ensure proper handling and liability coverage, please review and complete the necessary agreement to provide insurance form, which can be found here: agreement to provide insurance form pdf. This is a crucial step for safeguarding our operations regarding this particular shipment.
The temperature should be documented on the receiving documents, alongside the date and time of the temperature check. Deviation from the expected temperature range requires immediate action.
- Record Keeping: Detailed records are essential for traceability and quality control. This includes noting the date and time of arrival, the supplier’s details, the quantity received, any discrepancies observed during the inspection, and the temperature readings. These records act as a comprehensive audit trail, allowing for easy tracking of the fish’s journey from origin to the establishment. This documentation ensures accountability and facilitates effective quality control procedures.
Necessary Paperwork and Documentation
Accurate documentation is vital for traceability and compliance. The required paperwork for a fish shipment includes the delivery note, invoice, and cold chain certificate.
- Delivery Note: This document provides details of the shipment, including the quantity, type of fish, and date of delivery.
- Invoice: This document provides the financial details of the shipment, including the cost and payment terms.
- Cold Chain Certificate: This certificate documents the temperature of the shipment throughout its journey. This is essential for maintaining the freshness and safety of the fish and ensuring adherence to halal standards.
Potential Problems and Handling
During the receiving process, several potential problems might occur. These issues should be addressed promptly and effectively to maintain quality and prevent safety hazards.
- Damaged or Spoiled Fish: Immediate rejection of damaged or spoiled fish is crucial to prevent any contamination or quality issues. Follow established procedures for handling rejected shipments, such as returning the shipment or separating the damaged portion for disposal. This proactive approach helps prevent potential health risks and ensures the safety of the establishment’s operations.
- Discrepancies in Quantity: If the quantity of fish received differs from the quantity indicated on the delivery note, this discrepancy should be immediately noted and documented. Contact the supplier promptly to resolve the issue and avoid any financial or logistical problems. Discrepancies should be thoroughly documented and resolved in accordance with established procedures and in line with halal principles.
- Temperature Violations: If the temperature of the fish is outside the acceptable range, the shipment must be rejected or quarantined to prevent contamination. The cause of the temperature violation should be investigated to prevent future occurrences. This ensures that the product maintains its quality and is suitable for consumption.
Receiving Process Checklist
This checklist helps ensure a systematic and thorough receiving process.
| Step | Action | Verification |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Verify Documentation | Delivery note, invoice, cold chain certificate |
| 2 | Visual Inspection | Condition, signs of damage, odor |
| 3 | Temperature Check | Accurate thermometer reading |
| 4 | Record Keeping | Detailed records of all observations |
| 5 | Discrepancy Resolution | Contact supplier for quantity discrepancies |
Fish Storage and Handling

Maintaining the quality and safety of frozen fish is crucial for a food establishment. Proper storage and handling practices are essential to prevent spoilage and ensure the fish remains fit for consumption. These procedures are not only important for customer satisfaction but also for maintaining the integrity of the business and complying with relevant health regulations.
Optimal Temperature Maintenance
Maintaining the correct temperature is paramount for preserving the quality and safety of frozen fish. Freezing fish at a sufficiently low temperature halts microbial growth and slows down enzymatic activity, which causes deterioration. Optimal storage temperatures for frozen fish typically range from -18°C to -25°C. This range ensures that the fish remains frozen solid, preventing the growth of harmful bacteria and minimizing quality loss.
Deviations from this range can lead to the formation of ice crystals, which can negatively impact the texture and taste of the fish.
Proper Handling and Storage of Different Fish Types
Different types of frozen fish may have varying storage requirements. Some types of fish may be more prone to freezer burn than others. Therefore, careful handling and storage are necessary to maintain the quality of each type. For example, oily fish may require extra protection from freezer burn, possibly through vacuum packaging or specialized storage containers.
First-In, First-Out (FIFO) Inventory Management
Implementing a FIFO inventory system for frozen fish is vital for maintaining freshness and minimizing waste. The FIFO system prioritizes using the oldest stock first, ensuring that the fish that have been frozen for the longest period are consumed before the newer ones. This method minimizes the risk of consuming fish that have been frozen for an extended period, which can impact its quality.
This is a vital principle in food safety management and helps prevent any issues associated with the deterioration of fish quality over time.
Essential Storage Equipment
Appropriate storage equipment is critical for maintaining the optimal storage conditions for frozen fish. This includes deep-freezers, blast freezers, and appropriate containers and packaging. Deep freezers provide a consistent temperature environment for long-term storage, while blast freezers can rapidly freeze fish, reducing the risk of ice crystal formation. Proper packaging is essential for preventing freezer burn and maintaining the freshness of the fish.
For example, vacuum-sealed packaging can minimize exposure to air and prevent freezer burn.
Thawing Frozen Fish: A Safe Procedure
Thawing frozen fish must be done safely to prevent microbial growth. The safest method is to thaw the fish in the refrigerator. Thawing fish at room temperature should be avoided, as this creates a temperature danger zone, increasing the risk of bacterial growth. The thawing process should be carefully monitored to ensure the fish does not remain in the temperature danger zone for extended periods.
Potential Risks of Improper Storage and Handling
Improper storage and handling of frozen fish can lead to several potential risks. These include freezer burn, microbial growth, and a loss of quality and texture. Freezer burn occurs when the fish is exposed to air in the freezer, causing the surface to dry out and become damaged. Microbial growth can occur if the fish is not stored at a sufficiently low temperature.
This can lead to food poisoning if the fish is consumed. Maintaining proper storage procedures is vital for minimizing these risks.
Quality Control
Ensuring the quality of the frozen fish is crucial for maintaining the health and safety of consumers. A robust quality control plan is essential to identify potential issues and ensure the product meets the required standards. This plan should be integrated into the entire process, from receiving the shipment to final distribution.A comprehensive quality control system involves meticulous checks at each stage of the process.
This system should be structured to prevent contamination and maintain the integrity of the frozen fish. It is a crucial step in ensuring the overall quality and safety of the product, protecting both the establishment and its customers.
Quality Check Plan
The quality control plan should encompass all stages of the process. This includes a detailed inspection of the incoming shipment, regular checks during storage, and final checks before distribution. A systematic approach is vital for maintaining consistent quality standards.
Methods for Determining Fish Quality
Several methods can be used to assess the quality of frozen fish. Visual inspection, checking for any signs of damage or discoloration, is a fundamental step. Furthermore, temperature monitoring throughout the storage process is vital. The fish should be regularly checked for temperature to ensure that the freezing point is maintained, and to ensure that the quality is not compromised.
The use of specialized tools like thermometers ensures accuracy in these measurements. Testing for microbial contamination and bacterial growth is critical for determining the safety and quality of the fish. The presence of any abnormal smells or tastes also needs to be meticulously noted.
Comparison of Quality Control Measures
Various quality control measures can be employed, including visual inspection, temperature monitoring, microbial testing, and sensory analysis. Visual inspection is a quick and easy way to identify obvious defects, while temperature monitoring ensures that the freezing point is maintained. Microbial testing identifies potential health risks, and sensory analysis assesses the taste and smell of the fish. Each method provides valuable information about the quality of the frozen fish.
Table of Potential Defects and Corresponding Actions
| Defect | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Damaged Packaging | Packaging shows signs of damage, such as tears or punctures. | Reject the shipment; contact the supplier. |
| Abnormal Color | Fish exhibits unusual discoloration or discoloration. | Reject the shipment; contact the supplier. |
| Inadequate Freezing | Fish shows signs of thawing or insufficient freezing. | Reject the shipment; determine the cause. |
| Unpleasant Odor | Fish has an unusual or unpleasant odor. | Reject the shipment; contact the supplier. |
| Excessive Ice Crystals | Fish shows excessive ice crystals. | Assess the impact on quality. Potentially accept if the quality remains acceptable; document. |
Acceptance and Rejection Criteria
Establishing clear criteria for accepting or rejecting a shipment is vital. These criteria should be based on predefined standards and should be consistently applied. A shipment should be rejected if it shows signs of damage, contamination, or if the temperature during transport or storage was inconsistent with safety standards. If the fish exhibits any of the defects described in the table above, the shipment must be rejected.
If the quality is satisfactory, the shipment can be accepted. Documenting the reasons for acceptance or rejection is crucial for tracking and improvement.
Quality Control Data Tracking System
A robust system for tracking and recording quality control data is essential. This system should include detailed records of the date, time, and nature of the inspection, the results of the tests, and any actions taken. A standardized log should be maintained for each shipment. This record-keeping process enables monitoring trends and identifying potential problems or areas for improvement.
It facilitates efficient problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Food Safety and Regulations
Maintaining the safety of frozen fish is paramount in a food establishment. Adherence to food safety regulations ensures the well-being of consumers and protects the reputation of the business. This section Artikels the critical aspects of food safety relevant to frozen fish, from storage to handling procedures. These practices are essential to maintaining a high standard of halal food preparation and upholding the trust of customers.Food safety regulations are crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of the community.
They act as a safeguard, ensuring that food products are handled and prepared in a manner that minimizes the risk of contamination and illness. These regulations are meticulously crafted to prevent foodborne illnesses and maintain public trust in the food supply chain.
Overview of Food Safety Regulations
Food safety regulations vary by jurisdiction but generally require adherence to specific temperature controls, handling procedures, and record-keeping practices for frozen fish. These regulations aim to prevent bacterial growth and contamination. Proper temperature control and hygiene practices are essential components of maintaining food safety. These regulations often include specific requirements for the storage, handling, and preparation of frozen fish to ensure its safety for human consumption.
Importance of Adhering to Food Safety Guidelines
Adherence to food safety guidelines is not merely a regulatory requirement but a moral obligation. By complying with these guidelines, the establishment demonstrates its commitment to providing safe and wholesome food products to its customers. A commitment to food safety safeguards the reputation of the business and fosters customer trust. Non-compliance can lead to significant consequences, including legal penalties and damage to the establishment’s reputation.
Procedures for Maintaining a Safe Environment
Maintaining a clean and sanitary environment is crucial for preventing contamination. Regular cleaning and sanitization of all surfaces and equipment that come into contact with frozen fish are essential. This includes floors, walls, tables, and storage areas. Proper waste disposal procedures must be implemented to avoid cross-contamination and the accumulation of pathogens. Staff training on proper hygiene practices, such as handwashing and personal protective equipment (PPE) use, is also crucial.
Implementing proper waste management practices, including designated areas for waste disposal and proper containerization, is an integral part of maintaining a safe environment.
Procedures for Handling Potential Food Safety Issues
A well-defined protocol for handling potential food safety issues is essential. This protocol should include procedures for identifying, reporting, and correcting any deviations from established safety procedures. Prompt reporting of potential hazards or suspected contamination is crucial. Thorough documentation of all incidents is also critical for investigation and corrective actions. This includes recording the date, time, nature of the issue, and corrective actions taken.
This system enables the establishment to identify trends and implement preventive measures to minimize future occurrences.
Potential Hazards During Handling and Storage
| Hazard Category | Specific Hazards | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Fluctuation | Thawing/Freezing Cycles | Repeated freezing and thawing cycles can lead to bacterial growth and compromised quality. |
| Cross-Contamination | Contaminated Tools/Equipment | Contaminated tools or equipment used for handling other food items can transfer pathogens to frozen fish. |
| Improper Storage | Inadequate Temperature Control | Storing frozen fish above or below the designated temperature range allows for microbial growth and deterioration. |
| Poor Hygiene Practices | Lack of Handwashing | Insufficient handwashing or lack of hygiene by staff can introduce pathogens. |
| Pest Infestation | Rodents, Insects | Pest infestations can contaminate the fish with pathogens and parasites. |
Precautions for Preventing Cross-Contamination
Implementing rigorous measures to prevent cross-contamination is critical. Using separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked fish is vital. Proper handwashing procedures and the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) should be strictly enforced. This includes the use of gloves and dedicated aprons for handling raw fish. Designated areas for raw and cooked food preparation are important to avoid contamination.
Proper cleaning and sanitizing of all equipment and surfaces is a crucial preventive measure. This systematic approach minimizes the risk of cross-contamination.
Inventory Management
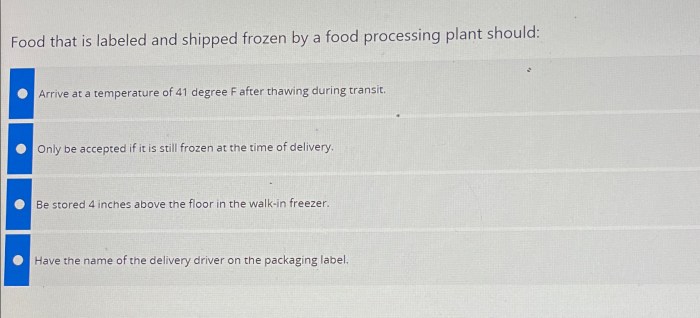
Maintaining an accurate inventory of frozen fish is crucial for operational efficiency and profitability. A well-structured system ensures that the establishment has the right amount of fish available at all times, minimizing waste and maximizing profitability. This careful management ensures that the supply meets demand, while preventing overstocking, which can lead to spoilage and financial losses.
Inventory Tracking System
A robust system for tracking frozen fish inventory is essential. This system should include detailed records of each shipment, noting the date received, quantity, type of fish, lot number, and estimated expiry date. This information should be meticulously documented to allow for easy retrieval and analysis of data. Using a spreadsheet program or dedicated inventory management software will aid in organizing this information effectively.
Calculating Order Quantities
Determining the appropriate amount of fish to order involves analyzing past sales data. Historical sales records provide valuable insights into seasonal fluctuations and demand patterns. Analyzing sales trends over a period (e.g., monthly, quarterly) helps predict future needs. A formula for calculating optimal order quantities can be based on past demand, lead time, and safety stock. A safety stock is an additional amount of inventory held to compensate for unexpected surges in demand or delays in delivery.
For example, if past sales data shows a consistent increase in demand during Ramadan, the establishment should anticipate this increase and order accordingly.
Inventory Data Template
A standardized template for recording inventory data will ensure consistency and accuracy. The template should include columns for the date of the shipment, the type of fish, the quantity received, the lot number, the estimated expiry date, and the quantity currently in stock. This structured template will streamline the inventory management process, allowing for quick and accurate data retrieval.
An example of a template could include:
| Date Received | Fish Type | Quantity Received | Lot Number | Expiry Date | Quantity in Stock |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024-07-27 | Salmon | 100 kg | ABC123 | 2024-09-15 | 100 kg |
| 2024-07-28 | Cod | 150 kg | DEF456 | 2024-09-20 | 150 kg |
Preventing Stock Loss and Waste
Proper storage and handling procedures are critical for minimizing stock loss and waste. Ensuring proper temperature control and avoiding contamination are crucial to maintaining the quality and freshness of the fish. Implementing FIFO (First-In, First-Out) inventory management, rotating stock to use older items first, is essential. Regular checks for any signs of spoilage are vital. Furthermore, utilizing appropriate packaging and storage containers will contribute to the prevention of damage and spoilage.
By implementing these strategies, the establishment can reduce waste and maximize the shelf life of the fish.
Importance of Accurate Inventory Records
Accurate inventory records are vital for effective financial management. They provide a precise picture of the available stock, enabling accurate cost accounting and pricing decisions. Inventory records facilitate efficient purchasing decisions, minimizing the risk of overstocking or understocking. This precision in data management allows the establishment to optimize its procurement strategies and meet the demands of the market effectively.
Forecasting Fish Demand
Forecasting fish demand requires careful consideration of various factors. These factors include seasonal variations, market trends, and competitor activities. Analyzing sales data from previous periods, understanding the trends and patterns, is key. Understanding the local market dynamics, such as religious observances or cultural preferences, will help refine the forecast. For example, a surge in demand for specific types of fish during particular festivals or events should be accounted for in the forecast.
By taking these factors into account, the establishment can make informed decisions regarding ordering and inventory management.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Accurate documentation is crucial for maintaining the integrity of fish shipments and ensuring compliance with food safety regulations. Proper record-keeping allows for traceability of the fish from origin to consumption, facilitating swift identification and resolution of potential issues. This detailed system ensures accountability and allows for efficient audits and analyses.
Necessary Forms and Records
Maintaining a comprehensive record system for fish shipments is vital for traceability and compliance. These records act as a testament to the quality and safety of the products, while simultaneously offering a framework for swift problem resolution. Specific forms and records are essential for tracking shipments from the moment they arrive at the establishment until they are distributed.
- Shipment Receipt Form: This form documents the arrival of the shipment, including the date, time, supplier details, truck number, and the quantity and condition of the fish upon delivery. This record aids in establishing a precise timeline and condition assessment upon receipt.
- Fish Inspection Log: This log details the inspection of the fish upon arrival, noting the temperature of the fish, any visible damage, and the results of quality checks. A log of any discrepancies, alongside corrective actions taken, should be recorded.
- Temperature Monitoring Records: Continuous monitoring of the fish’s storage temperature is critical. Detailed logs, with timestamps, record the temperature of the fish throughout the storage process. Any deviation from the required temperature range should be meticulously noted.
- Handling Procedures Log: This log meticulously records all handling procedures, ensuring adherence to established protocols. This includes the time of each handling step, the personnel involved, and any deviations from the standard operating procedure (SOP).
Storing and Retrieving Shipment Records
A well-organized system for storing and retrieving shipment records ensures easy access to information when needed. This organized system allows for quick retrieval of relevant records, supporting efficient operations and problem-solving.
- Designated Storage Area: Records should be stored in a secure, climate-controlled area, protected from damage and unauthorized access. Regular backups and offsite storage should also be considered.
- File Organization System: A standardized file organization system should be implemented, categorizing records by shipment date, supplier, or other relevant criteria. A clear filing system ensures records are easily located.
- Database Management: Implementing a digital database for storing and managing shipment records can streamline the process. This database allows for easy search, retrieval, and reporting. Software solutions should be chosen with the ability to export reports in different formats.
Ensuring Data Accuracy and Integrity
Data accuracy and integrity are paramount to maintaining trust and complying with regulations. This systematic approach guarantees that records are accurate and reliable, supporting efficient business operations and regulatory compliance.
- Verification Procedures: Implementing verification procedures for all records, ensuring accuracy and minimizing errors. This should include double-checking data entries, cross-referencing information, and using standardized formats.
- Data Validation: Using validation checks to ensure data integrity. These checks can include data range validation and cross-referencing data with other records.
- Regular Audits: Regular audits of records should be performed to ensure accuracy and compliance with regulations. This helps maintain the integrity of the data and detects potential errors or inconsistencies.
Traceability Examples
Traceability is critical for tracking fish from origin to consumption. A robust system is crucial for identifying any potential issues.
- Supplier Information: Include the supplier’s name, address, and contact information. This information is essential for tracing the origin of the fish.
- Lot Numbers: Assign unique lot numbers to each shipment to track the specific batch of fish. This is a critical part of the traceability system.
- Dates and Times: Include the date and time of receipt, inspection, handling, and storage to maintain a comprehensive timeline.
Types of Records Needed
A clear understanding of the various records needed ensures a comprehensive system.
| Record Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Shipment Receipt Form | Details shipment arrival. |
| Inspection Log | Records fish condition upon arrival. |
| Temperature Logs | Monitors temperature throughout storage. |
| Handling Procedures Log | Records all handling activities. |
| Quality Control Reports | Documents quality checks and results. |
Archiving Important Documents
Archiving important documents protects against loss and ensures future reference.
- Secure Storage: Store records in a secure, climate-controlled environment, protecting them from damage and unauthorized access.
- Retention Policy: Establish a clear retention policy outlining the length of time records must be kept. This ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Backup Procedures: Implement regular backups of records, both on-site and off-site. This ensures that data is protected from loss due to hardware failure or natural disasters.
Environmental Considerations
Ensuring the sustainability of our operations is paramount. Handling a shipment of frozen fish carries environmental implications that must be thoughtfully addressed. Minimizing our impact on the planet aligns with our commitment to responsible practices and long-term sustainability, while also adhering to the principles of Islamic teachings on stewardship of resources.Understanding the environmental footprint of our operations allows us to proactively seek solutions that minimize harm to the environment.
This includes exploring various methods for sustainable sourcing, responsible packaging, and efficient waste management. These practices not only protect the environment but also contribute to the overall well-being of the community and future generations.
Transportation Impact
The transportation of frozen fish, particularly over long distances, contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. The use of fuel-efficient vehicles and optimizing transport routes can reduce these emissions significantly. Careful planning and logistics are crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of transportation. Examples of this include utilizing alternative fuels, exploring multimodal transport options, and strategically locating distribution centers.
Storage Impact
Maintaining a consistent temperature during storage is crucial for preserving fish quality but can also consume energy. Employing energy-efficient refrigeration systems and optimizing storage practices, such as proper insulation, can minimize energy consumption. Using renewable energy sources for refrigeration is an additional step towards a more sustainable approach.
Waste Management Practices
Proper waste management is essential. Waste from packaging, fish processing, and other activities must be handled responsibly. Recycling and composting programs for organic waste should be implemented to minimize landfill waste. This is crucial as it prevents the accumulation of non-biodegradable waste and reduces environmental pollution. Implementing effective waste segregation protocols is vital for efficient recycling and composting.
Sustainable Sourcing Options
Prioritizing sustainable fisheries is vital for the long-term health of marine ecosystems. Choosing suppliers who practice sustainable fishing methods, adhering to catch limits, and promoting responsible aquaculture practices are essential. Supporting fisheries certified by reputable organizations demonstrates a commitment to ethical and environmentally conscious sourcing.
Responsible Sourcing in the Food Industry
Responsible sourcing is crucial for the food industry. Choosing suppliers who prioritize environmental protection and social responsibility is a vital aspect of ethical operations. By supporting sustainable practices, businesses contribute to the well-being of both the environment and the communities involved in the supply chain. This approach is essential for upholding ethical standards in the industry and adhering to Islamic principles of fairness and justice.
A shipment of frozen fish has arrived at the establishment. Given the delicate nature of the goods, it’s crucial to immediately check the condition of the shipment. If any damage is observed, you should contact Mendota Insurance’s claims department at mendota insurance claims phone number for guidance and to initiate a claim process. This proactive step will help ensure the establishment’s ability to handle the fish appropriately and avoid any potential losses.
Packaging Options Comparison
| Packaging Material | Environmental Impact (Lower is Better) | Cost | Durability | Recyclability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Cardboard | Low | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Biodegradable Plastic | Moderate | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Expanded Polystyrene | High | Low | High | Low |
Note: The table provides a simplified comparison. A comprehensive evaluation considers various factors specific to each packaging material.
Final Wrap-Up
So, a shipment of frozen fish arrives at your food establishment? This guide equipped you with the knowledge to handle the entire process efficiently and safely. From meticulous receiving procedures to advanced inventory management techniques, you’re now prepared to handle every stage of the fish journey. Remember, proper handling, storage, and quality control are paramount to maintaining food safety and customer satisfaction.
Let’s make sure your fish is always fresh and delicious!
Question Bank
What’s the best way to prevent cross-contamination during fish handling?
Use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw fish to avoid cross-contamination with other foods. Thoroughly wash your hands and surfaces frequently with hot, soapy water.
How often should I check the temperature of the fish during unloading?
The frequency of temperature checks depends on the size of the shipment and the storage conditions. A good rule of thumb is to check the temperature at multiple points throughout the unloading process to ensure the fish is consistently within the safe temperature range.
What are some common problems during fish receiving, and how do I handle them?
Damaged packaging, incorrect temperatures, or paperwork discrepancies are potential problems. Always document any issues immediately and follow your establishment’s protocol for handling such situations. Contact the supplier for resolution as needed.
What are the environmental concerns when storing frozen fish?
Consider using eco-friendly packaging, optimizing storage space to reduce energy consumption, and implementing proper waste management procedures to minimize the environmental impact of frozen fish storage.
